Understanding Web3: The Decentralized Internet
Understanding Web3: The Future of the Internet
Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, introducing decentralization, user ownership, and trustless transactions. It challenges the traditional Web2 model by distributing power among users rather than centralized entities.
At its core, Web3 is built upon blockchain technology, enabling transparent, verifiable, and permissionless interactions across the web.
From Web1 to Web3: A Brief Evolution
The internet has evolved through three major phases: Web1 (static and read-only), Web2 (interactive and social), and now Web3 (decentralized and trustless). Each phase transformed how information and value flow online.
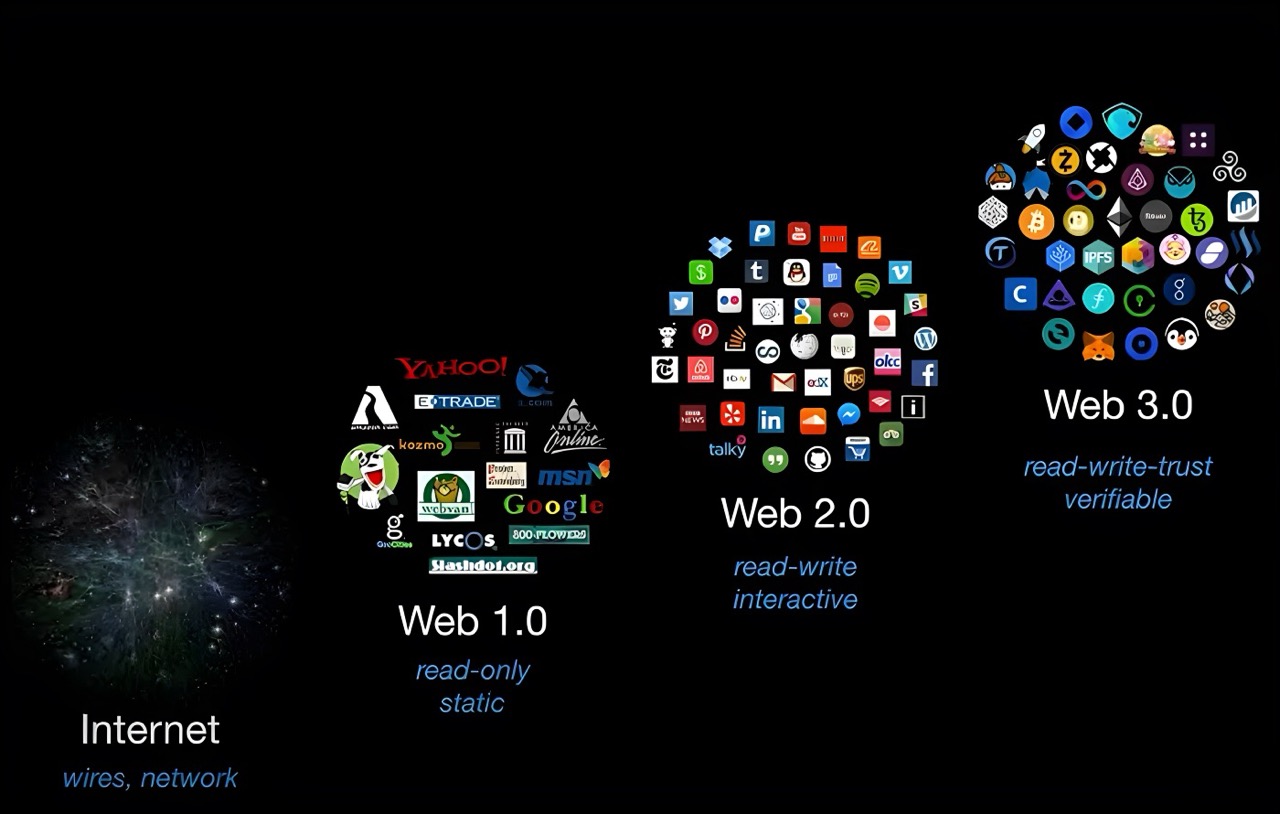
The transition from static Web1 to interactive Web2 and decentralized Web3.
Core Technologies Behind Web3
Web3 relies on several foundational technologies that ensure its decentralized nature. These include blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized storage systems.
Key Components
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger that records transactions transparently.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements without intermediaries.
- Cryptographic Wallets: Secure tools for user identity and asset management.
- Decentralized Storage: Systems like IPFS that eliminate single points of failure.
Web3 eliminates intermediaries — allowing peer-to-peer ownership, payments, and governance — creating a more democratic digital ecosystem.
Getting Started with Web3 Development
Developers can interact with blockchain networks using frameworks like Hardhat, Truffle, or Remix. Below is a basic example of a Solidity smart contract.
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract HelloWeb3 {
string public message = #ce9178;">'Hello, Web3 World!';
function updateMessage(string memory newMessage) public {
message = newMessage;
}
}A simple 'Hello Web3' smart contract written in Solidity.
Once compiled and deployed, users can interact with this contract directly through a Web3 wallet like MetaMask, or programmatically using libraries such as web3.js or ethers.js.
import { ethers } from #ce9178;">'ethers';
const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
const contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, abi, provider.getSigner());
const msg = await contract.message();
console.log(msg);Connecting to a deployed smart contract using Ethers.js.
Real-World Applications of Web3
Use Cases
| Sector | Example | Impact |
| Finance | DeFi protocols (Uniswap, Aave) | Enables permissionless lending and trading |
| Art & Media | NFTs | Empowers creators to monetize digital ownership |
| Gaming | Play-to-Earn platforms | Creates real asset ownership for players |
| Governance | DAOs | Facilitates decentralized decision-making |
Web3 bridges technology and philosophy — it’s not just a technical upgrade but a shift in how we perceive ownership and trust online.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, Web3 faces challenges such as scalability, energy consumption, user experience, and regulatory uncertainty. Overcoming these issues will define its adoption curve in the coming decade.
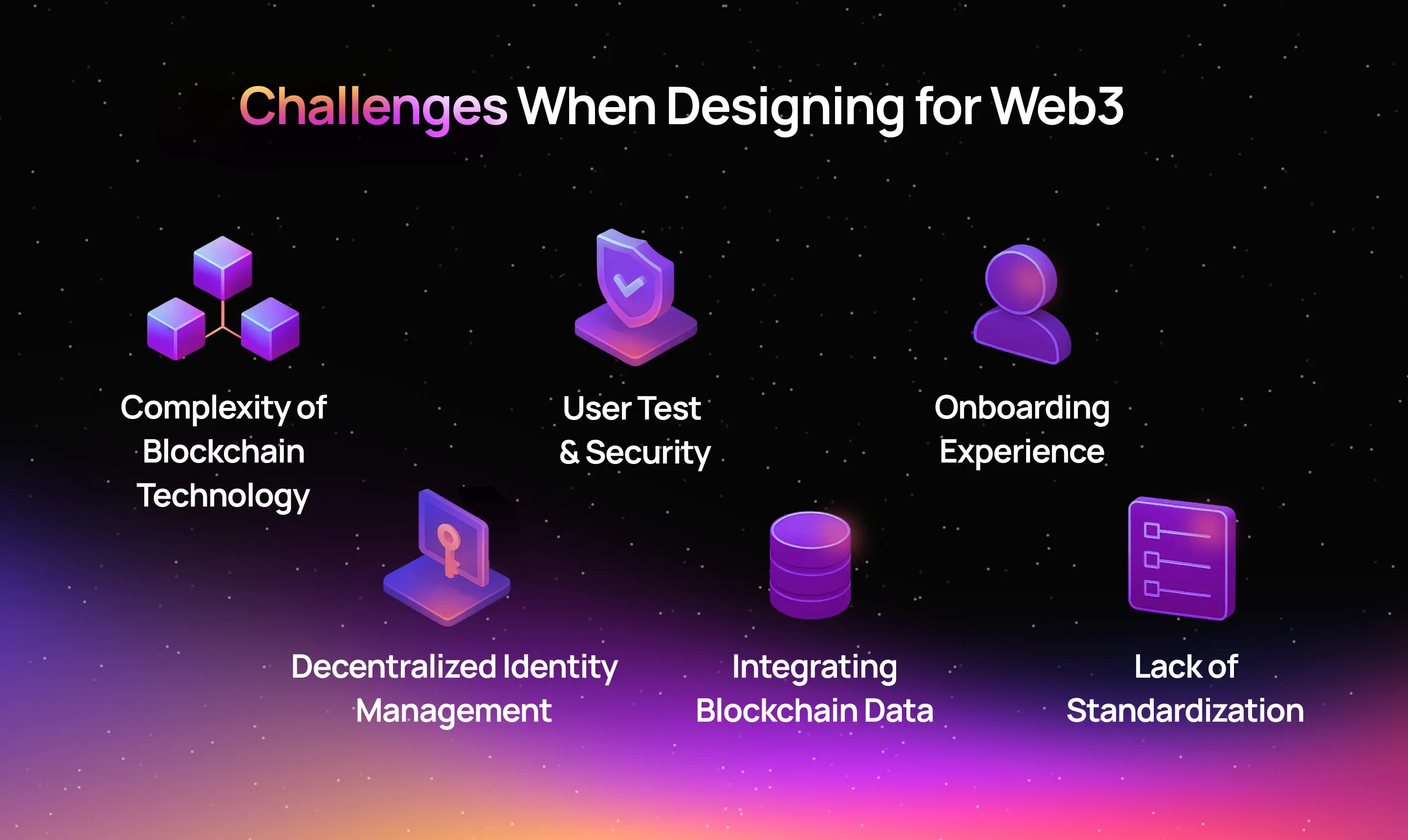
Scalability and UX remain major bottlenecks for mainstream Web3 adoption.
Conclusion
Web3 is redefining the digital economy through decentralization and transparency. Although still in its early stages, it promises a future where users truly own their data, identities, and digital assets — shaping a more open and equitable internet.